With global healthcare systems offering diverse training structures, understanding the difference between MD (Doctor of Medicine) and DM (Doctorate of Medicine) becomes essential to take your career plan ahead.
So, we are going to cover all the details that clear every doubt, including:
- What are MD and DM?
- What is the key difference between MD and DM?
- Complete Medical Education Pathway
- Scope of MD vs DM
- eligibility criteria
- Admission Process
- MD vs DM international Career perspective
- Career Opportunities
So, if you are planning to pursue your career after MBBS or want to get a global recognised medical degree to work abroad as a medical professional, this is the best blog to read.
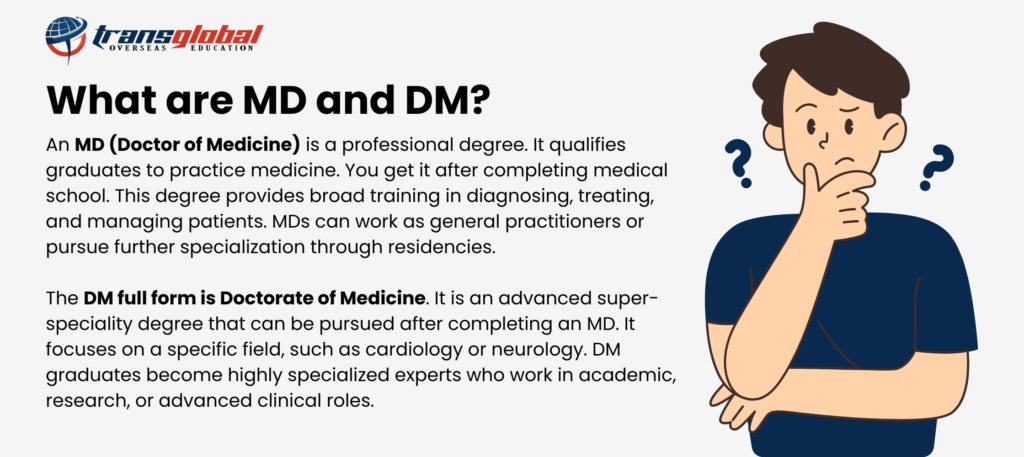
What are MD and DM in Medical?
MD (Doctor of Medicine) and DM (Doctorate of Medicine) are postgraduate medical degrees pursued after MBBS. While MD provides broad clinical specialization, DM focuses on advanced super-specialty training. Understanding the difference helps doctors choose the right path for their medical and international career goals.
MD Full Form in Medical
Doctor of Medicine is the full form of MD, which is a postgraduate medical degree pursued after completing an MBBS. The meaning of MD in medicine refers to advanced training that allows a doctor to specialize in a broad clinical field. An MD doctor is a physician trained in areas such as Internal Medicine, Pediatrics, Pathology, Radiology, or other major medical disciplines.
In simple terms, MD is the first level of specialization after MBBS, helping doctors gain in-depth clinical knowledge and opening opportunities for senior hospital roles, teaching, research, and international medical practice.
DM Full Form in Medical
DM full form in medical is Doctorate of Medicine. It is a super-specialty medical degree pursued only after completing an MD. The meaning of DM in medical education refers to advanced and focused training in a specific, high-skill area of medicine. A DM doctor is a specialist with deep expertise in a narrow field, such as DM Cardiology, DM Neurology, DM Gastroenterology, DM Nephrology, or DM Oncology. The DM degree equips doctors to manage complex cases, work in tertiary care hospitals, and pursue advanced clinical or academic roles. DM is not a replacement for MD; it is a higher level of specialization after MD.
MD vs DM: Key Differences Explained
MD builds your foundation as a specialist, while DM makes you an expert in a sub-specialty.
Here is the major difference that help you to understand between the MD and DM:
| Aspect | MD | DM |
| Degree Type | Postgraduate | Super-Specialty |
| Eligibility | After MBBS | After MD |
| Duration | 3 years | 2–3 years |
| Scope | Broad specialization | Highly focused expertise |
| Example Fields | Medicine, Pediatrics, Radiology | Cardiology, Neurology, Gastroenterology |
| Career Level | Specialist Doctor | Super-Specialist Doctor |
The medical education pathway to becoming a super-specialist follows a structured sequence:
Complete Medical Education Pathway
MBBS → MD → DM
MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) is the foundational medical degree that qualifies a student to practice as a general doctor.
After MBBS, doctors must pursue MD (Doctor of Medicine), which provides postgraduate specialization in a broad medical field.
Only after completing an MD can a doctor apply for DM (Doctorate of Medicine), a super-specialty degree offering advanced, focused training.
DM cannot be pursued directly after MBBS; MD is mandatory before DM, making this step-by-step pathway essential for super-specialization.
Scope of MD vs DM in Medical Career
Career scope comparison is essential before making any decision. Here is a guide for you to understand the care scope for MD and DM.
Scope After MD
The scope of an MD degree in the medical career is broad and rewarding. After completing an MD (Doctor of Medicine), doctors can work as consultant physicians or hospital specialists in both government and private healthcare institutions. MD graduates also have strong opportunities in medical teaching as lecturers or professors, as well as in clinical and academic research roles. With the required licensing exams, MD doctors can plan a stable medical career, especially in core specialties such as:
- General Medicine
- Pediatrics
- Radiology
- Pathology
Where demand remains consistently high across healthcare systems worldwide.
Scope After DM
The scope after completing a DM (Doctorate of Medicine) is highly advanced and specialized. DM graduates work as super-specialist consultants in their chosen fields and are eligible for high-paying clinical roles, especially in private and corporate hospitals. They are in strong demand in tertiary care and super-specialty hospitals, where complex and critical cases are treated. DM doctors also have excellent opportunities in advanced medical research, academics, and teaching at leading institutions.
Globally, DM and DM-equivalent specialists are highly valued in developed healthcare systems. DM doctors commonly specialize in:
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Oncology
- Gastroenterology
Fields known for higher international demand, global mobility, and competitive salaries.
Read Also : Best Low-Cost MBBS Universities Abroad for Indian Students
MD or DM: Which One Should You Choose?
Ultimately, MD vs DM is not about which degree is better or worse—it is about aligning your education with your long-term career goals and interests. So;
Choose MD if:
You should choose MD (Doctor of Medicine) if your goal is to start your medical career earlier and gain practical experience without spending additional years in super-specialization. MD is ideal for doctors who prefer a broader medical practice rather than focusing on a narrow specialty. It is also a strong option if you plan to pursue an MD abroad and practice internationally, as MD or equivalent residency programs are widely recognized across countries. Additionally, MD offers greater career flexibility, allowing opportunities in clinical practice, teaching, research, hospital administration, and global healthcare systems.
Choose DM if:
You should choose DM (Doctorate of Medicine) if you aim to become a super-specialist with deep expertise in a specific medical field. DM is ideal for doctors who want advanced clinical training and wish to treat complex and critical cases. It is the right choice if you plan to work in top global hospitals, super-specialty centers, or tertiary care institutions. DM doctors are also eligible for higher specialization-based income, as super-specialists are in high demand worldwide.
Read Also : Top MS & MSc Programs in the UK
Eligibility Criteria for MD and DM
Whether you planning to MD or DM abroad, you need to fulfill following eligibility to pursue;
| Criteria | MD Eligibility (Abroad) | DM Eligibility (Abroad) |
| Basic Qualification | Completed MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) from a recognized medical university | Completed MD (Doctor of Medicine) in a relevant specialty |
| Internship Requirement | Mandatory completion of 1-year internship (recognized by the host country) | Internship already covered during MBBS & MD |
| Academic Performance | Minimum qualifying marks as per university or country norms (often 50–60%) | Strong academic record in MD with specialization relevance |
| Entrance Exams | Country-specific exams or evaluations (e.g., university tests, licensing pathways) | Entrance exams or institution-based selection/interviews |
| Language Proficiency | Proof of language proficiency (IELTS/TOEFL or local language, depending on country) | Language requirements may apply, especially for patient-facing roles |
| Clinical Experience | Not mandatory but preferred in some countries | Relevant clinical experience strongly preferred |
| Medical Registration | MBBS degree recognized by the host country’s medical council | MD degree must be recognized for super-specialty training |
| Seat Availability | Widely available across multiple countries | Limited seats due to super-specialty nature |
| Visa & Documentation | Student visa, medical fitness, and academic documents required | Study or training visa with institutional sponsorship |
Admission Process for MD and DM Abroad
Here are the process of MD and DM abroad:
MD Abroad Admission Process
The admission process for MD abroad follows a systematic approach. Such as:
- Research Programs: Shortlist universities by comparing curriculum structure, clinical training, global recognition, tuition fees, and long-term career opportunities.
- Entrance Exams: Appear for required exams such as USMLE, MCAT, PLAB, or language proficiency tests like IELTS/TOEFL, depending on the destination country.
- During Submission of Application: Academic transcripts along with essential documents ( including SOP, LORs, CV, and personal statements).
- Interviews: Some universities conduct online or in-person interviews to assess academic background, communication skills, and motivation.
- Acceptance & Visa: After receiving the offer letter, you need to accept it. Next, you have to get a student visa to study in the country. You also need to check health, financial, and legal documentation before departure.
This structured process ensures transparency and preparedness for studying MD abroad.
Admission Process for DM Abroad
The admission process for DM, AKA Doctorate of Medicine, is very structured and competitive. To pursue that, you need to focus on academic excellence and clinical expertise. Along with that, here is the list of eligibility criteria for your DM abroad:
- Meet Eligibility Criteria: Vital to have a recognized MD or equivalent postgraduate degree in a relevant specialty, along with adequate clinical experience.
- Entrance Exams: Applicants are required to qualify super-specialty entrance exams such as NEET SS, AIIMS SS, or JIPMER, depending on the institution or country.
- During the Application Submission: Have an academic transcript, LORs, a detailed SOP, and clinical experience records.
- Interviews: Some universities may conduct interviews to assess clinical knowledge, specialization interest, and professional goals. So, you need to clear it to get admission in a DM degree.
- Visa & Enrollment: After receiving the admission offer, complete visa application procedures, submit required documents, and finalize enrollment with the institution.
This process ensures that only qualified and committed doctors advance into super-specialty medical training.
MD vs DM Abroad: International Career Perspective
In the international medical field, you need to know that many countries, like the USA, UK, do not follow the exact MD–DM structure used in India.
Instead, international medical education systems offer MD or MD-equivalent residency programs for specialization and advanced fellowship or sub-specialty programs that serve as equivalents to DM.
These globally recognized pathways provide extensive clinical training, international exposure, and strong career mobility.
Understanding how MD and DM translate internationally helps you as a doctor choose the right country, training route, and long-term career strategy for practicing medicine abroad.
Study MD Abroad
Studying MD abroad offers global exposure, advanced clinical training, and internationally recognized qualifications. With diverse specialization options and strong career prospects, MD abroad is an ideal pathway for doctors aiming to build a successful international medical career.
Countries for MD Abroad
Below is a comprehensive table of countries offering MD (Doctor of Medicine) or MD-equivalent programs for Indian students.
| Country | Key Highlights of MD Programs |
| United States | World’s most advanced medical education system, MD via residency pathway, excellent clinical exposure, high global recognition, requires USMLE |
| United Kingdom | Structured postgraduate training, strong NHS exposure, MD/MS or specialty training routes, PLAB required for practice |
| Germany | Tuition-free or low-cost education, high-quality healthcare system, strong clinical training, German language required |
| Canada | High academic standards, limited seats, research-focused MD programs, excellent global reputation |
| Australia | MD programs aligned with global standards, strong clinical training, good post-study work options |
| United Arab Emirates (Dubai) | Modern healthcare infrastructure, growing demand for doctors, international faculty, English-taught programs |
| Poland | English-taught MD programs, EU recognition, affordable fees, popular among international students |
| Georgia | Budget-friendly education, English-medium programs, increasing global recognition |
| Philippines | US-pattern medical education, English instruction, popular with international and Indian students |
Fees for MD Abroad
Below is an indicative fee table of MD or MD equivalent medical degrees. Fees are approximate and meant for international students, as exact costs vary by residency status, program structure, and year.
| Country | MD / MD-Equivalent Program | Approximate Annual Fees |
| United States | MD (Graduate Entry) | USD 60,000 – 75,000 |
| United Kingdom | MD / Clinical Medicine | GBP 35,000 – 55,000 |
| Germany | Medical Degree (MD-equivalent) | Low or No Tuition (Admin fees €300–500/semester) |
| Australia | MD (Graduate Entry) | AUD 75,000 – 90,000 |
| Canada | MD | CAD 25,000 – 55,000 |
| United Arab Emirates (Dubai) | MD | AED 90,000 – 160,000 |
| Poland | MD / MBBS (English-taught) | EUR 12,000 – 18,000 |
| Georgia | MD / MBBS | USD 6,000 – 10,000 |
| Philippines | MD (after Pre-Med) | USD 3,500 – 7,000 |
| India | MD (Post-MBBS) | INR 1–5 lakhs/year (Govt) INR 15–30 lakhs/year (Private) |
The above-mentioned fees do not include living expenses, insurance, or licensing exam costs.
Duration for MD Abroad
Every country has a different timeline to finish MD or equivalent degree.
| Country | MD / MD-Equivalent Duration | Key Notes |
| United States | 3–7 years | MD is completed through residency after graduation; duration depends on specialty |
| United Kingdom | 2–3 years (MD research) / 5–6 years (MBBS) | MD is mostly research-based; clinical training via MBBS & specialty routes |
| Germany | 5–6 years (medical degree) + specialty training | No separate MD title; specialization happens through residency |
| Australia | 4 years | Graduate-entry MD after a bachelor’s degree |
| Canada | 3–4 years | MD followed by residency; very limited seats for international students |
| United Arab Emirates (Dubai) | 4–5 years | US/UK-style MD programs with modern clinical exposure |
| Poland | 6 years (MD/MBBS equivalent) | English-taught programs, EU-recognized |
| Georgia | 6 years | Popular and affordable for international students |
| Philippines | 4 years MD (after pre-med) | US-pattern curriculum, English instruction |
Study DM Abroad
Studying DM abroad opens doors to advanced super-specialty training through fellowships and sub-specialty programs. It offers global recognition, cutting-edge clinical exposure, and high-demand career opportunities in top international hospitals and healthcare systems.
Countries for DM Abroad
Below is a country-wise table for DM (Doctorate of Medicine) or DM-equivalent super-specialty programs. In many countries, DM is offered as fellowships, sub-specialty residencies, or board-certified training rather than a degree titled “DM”.
| Country | DM / DM-Equivalent Pathway | Key Highlights |
| United States | Fellowship after Residency | World’s best super-specialty training, high salaries, strong global recognition, requires USMLE |
| United Kingdom | Specialty Training (ST) / Fellowships | NHS-based advanced training, structured pathway, global acceptance |
| Germany | Sub-Specialty Training after Residency | Tuition-free education, excellent clinical exposure, German language required |
| Canada | Fellowship Programs | Research-focused, limited seats, strong international credibility |
| Australia | Advanced Specialist Training | High-quality healthcare system, good post-training work options |
| United Arab Emirates (Dubai) | Fellowship / Board Programs | Modern hospitals, tax-free income, high demand for specialists |
| Germany | Sub-specialty Certification | Highly structured, EU-wide recognition |
| Singapore | Fellowship & Advanced Training | Asia’s top healthcare hub, strict selection, global exposure |
| France | DESC / Fellowship | Advanced specialization, EU recognition, language requirement |
Fees for DM / DM-Equivalent Programs Abroad
Since most countries offer DM as fellowships or super-specialty training, fees can vary widely based on hospital type and specialty.
| Country | DM / Equivalent Program Type | Approximate Fees |
| United States | Fellowship after Residency | USD 0 – 10,000/year (Often stipend-based) |
| United Kingdom | Specialty Training / Fellowship | GBP 5,000 – 25,000/year |
| Germany | Sub-Specialty Training | Low or No Tuition (Doctors are often salaried) |
| Australia | Advanced Specialist Training | AUD 10,000 – 40,000/year |
| Canada | Fellowship Programs | CAD 5,000 – 30,000/year |
| United Arab Emirates (Dubai) | Fellowship / Board Training | AED 40,000 – 120,000/year |
| Singapore | Fellowship & Advanced Training | SGD 10,000 – 35,000/year |
| France | DESC / Fellowship | EUR 3,000 – 15,000/year |
Duration to Pursue a DM program Abroad
Here is a table of time-duration for DMs in each country.
| Country | DM / Equivalent Program Type | Typical Duration |
| United States | Fellowship after Residency | 2–3 years |
| United Kingdom | Specialty Training (ST) / Fellowship | 2–5 years (depends on specialty) |
| Germany | Sub-Specialty Training | 2–3 years |
| Australia | Advanced Specialist Training | 2–4 years |
| Canada | Fellowship Programs | 1–3 years |
| United Arab Emirates (Dubai) | Fellowship / Board Programs | 2–3 years |
| Singapore | Fellowship & Advanced Training | 1–3 years |
| France | DESC / Fellowship | 2–4 years |
Career opportunities after MD vs DM Abroad
MD and DM have amazing career potential in the international world of medical science. Based on your career goal and eligibility you can pursue your desirable professional plan.
Below is a clear comparison table highlighting career opportunities after completing MD and DM abroad, helping students understand global job prospects and career growth.
| Aspect | After MD Abroad | After DM / DM-Equivalent Abroad |
| Primary Role | Specialist Doctor / Consultant | Super-Specialist Consultant |
| Clinical Practice | General & specialty hospitals | Tertiary care & super-specialty hospitals |
| Specialization Level | Broad specialization | Highly focused, advanced expertise |
| Common Job Titles | Physician, Specialist, Registrar | Cardiologist, Neurologist, Oncologist, Gastroenterologist |
| Academic Careers | Lecturer, Assistant Professor | Professor, Senior Academic Consultant |
| Research Opportunities | Clinical & academic research | Advanced research, clinical trials, innovation |
| International Mobility | High (after licensing exams) | Very high (global demand for super-specialists) |
| Work Settings | Hospitals, clinics, universities | Super-specialty centers, research institutes |
| Leadership Roles | Department coordinator | Department head, clinical director |
| Income Potential | Good & stable | Higher, specialization-based |
| Global Demand | Consistent across countries | Very high in developed healthcare systems |
Final Thoughts
MD and DM recreate a successful medical career. Your preference between MD and DM should be guided by your long-term career vision, interest in specialization, plans for international practice, and the time and financial investment you are willing to make. Choosing the right path ensures professional growth and long-term career satisfaction.
Study MBBS, MD & DM Abroad – Free Expert Consultation
Planning to study MBBS or MD abroad, or pursue DM-equivalent super-specialty training? Get free expert guidance on university selection, eligibility, admissions, visas, and licensing exams. Book your FREE consultation today and take the first step toward a successful global medical career.
Additional FAQs on MD vs DM in Medical Career
1. What is DM’s full form in medical?
DM full form in medical is Doctorate of Medicine. It is a super-specialty medical degree pursued after completing an MD and focuses on advanced training in a specific medical field.
2. What is the full form of MD in medical terms?
MD stands for Doctor of Medicine. It is a postgraduate medical degree pursued after MBBS that allows doctors to specialize in fields such as internal medicine, pediatrics, radiology, or pathology.
3. How to become eligible for MD programs abroad?
To pursue an MD program abroad, you need to have a recognized MBBS degree and an internship on a mandatory basis. Besides, you need to check by yourself or with an expert abroad study counselor to know country-specific entrance guidelines.
4. How to become eligible for DM programs abroad?
To apply for DM programs abroad, it is mandatory to have a recognized MD or equivalent postgraduate medical degree. Apart from this, you can check for country-specific requirements and licensing criteria where applicable.
5. What is the difference between MD and DM in medical education?
An MD is a Doctor of Medicine. It is a primary medical degree. On the other hand, DM stands for Doctorate of Medicine, which is a higher level of specialization.
6. How many years is the MD and DM course duration?
MD typically takes 3 years after MBBS. DM requires an additional 2–3 years after completing MD, depending on the specialty and country.
7. What does DM cardiology or DM neurology mean?
DM Cardiology and DM Neurology refer to super-specialty medical degrees. Here, the DM Cardiology focuses on heart-related diseases. On the other hand, DM neurology addresses neurological disorders.
8. Can MD or DM doctors work abroad?
Yes, you can work abroad after MD and DM. But you need to meet country-specific licensing requirements. Studying MD abroad or pursuing DM-equivalent fellowships internationally can significantly improve global career opportunities.
9. Which countries offer the best MD and DM programs for international students?
International students who want to study MD and DM programs can select from high-quality programs available in the UK, the USA, Australia and Canada.
10. Do I need an MD degree to pursue DM?
Yes. An MD degree (or an equivalent postgraduate medical qualification) is mandatory to pursue DM. DM is a super-specialty program and cannot be taken directly after MBBS.
11. What are the admission requirements for MD and DM programs abroad?
Below are the admission requirements for MD Programs Abroad:
- Recognized MBBS degree or bachelor’s degree in a science-related field
- Completion of mandatory internship as per the university or country guidelines
- Standardized entrance exams such as MCAT, UKCAT, or GAMSAT
- English language proficiency
- Academic transcripts
- Statement of Purpose (SOP)
- Personal Statement
- Letters of Recommendation (LORs)
Apart from holding a recognized MD or equivalent postgraduate medical degree, DM or DM-equivalent) programs abroad may require the following:
- Relevant clinical experience in the chosen specialty
- Valid medical registration/license in the home or host country
- Specialty-specific entrance exams or institutional assessments
- Language proficiency as per country
- Updated CV with clinical and research experience
- Research experience or publications
- LORs
- SOP
- Interview
- Medical fitness verification
- Background verification
- Visa
- Work/training permit compliance
These requirements vary by country, specialty, and training pathway.